By Alessandro Bacci.
Any opinions expressed are those of the author, and do not necessarily reflect the views of Iraq Business News.
Iraq’s Fifth Licensing Round: Some Preliminary Considerations After the Auction
On the morning and afternoon of April 26, 2018, I participated in a petroleum scholar workshop organized in London by the Association of International Petroleum Negotiators (A.I.P.N.). There I gave the presentation “Current Trends Concerning Petroleum Service Contracts in the Middle East.”
I explained the difficulties that Iraq was experiencing with its technical service contracts (T.S.C.s) and that, exactly while we were discussing in London, Iraq was holding in Baghdad its fifth licensing round after the introduction of some amendments to its service contracts in the previous weeks. After the end of the workshop, I stopped in café where I started collecting information concerning the results of the licensing round.
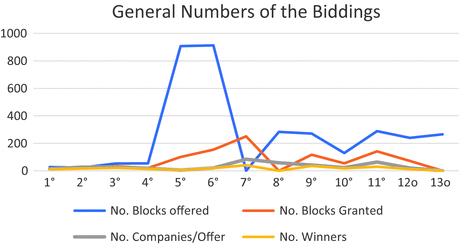
Iraq’s fifth licensing round was related to the offering of 11 blocks. In specific, 10 onshore blocks located along the Iraqi borders with Kuwait and Iran, and 1 offshore block in the Persian Gulf waters. In the end, six blocks were awarded, while five of the exploration blocks did not receive any bids. So, what is a correct evaluation of this fifth licensing round? Probably, a balanced answer would be that Iraq’s fifth licensing round ‘on the day of the auction’ obtained a mixed result.
In fact, if, on the one side, it’s true that six blocks were awarded, on the other side, it’s also true that no major international oil company (I.O.C.) won any bids. Of the big names in the petroleum industry, Italy’s E.N.I. alone decided to participate and made two unsuccessful bids. U.A.E.-based Crescent Petroleum obtained three blocks, China’s Geo-Jade two blocks, and China’s United Energy Group one block.
One initial explanation for the mixed result might be that the Iraqi government had previously changed the date of the auction. Initially, the Ministry of Oil wanted to have the auction in June 2018, but, then, it moved the date of receiving the offers of the international qualified companies for the licensing round forward to April 15. At the same time, the Oil Ministry’s Petroleum Contracts and Licensing Directorate sent the document concerning the final form of the tender, the conditions of the tender, and the formula of the exploration, development, and production contract (E.D.P.C.) and of the development production contract (D.P.C.) only on April 13.
However, when the Oil Ministry realized that the I.O.C.s—fourteen companies had purchased the documents required to participate in the bid round—would have had only two days to study the new contracts and submitting an offer, it postponed the deadline for submitting an offer to April 25. Then, the Oil Ministry held the licensing round on April 26. In any case, the time for studying the dossier relating to the 11 blocks was limited according to either deadline. On top of this, Iraq will hold its national elections on May 12, and, before committing to investing on a long-term basis in additional projects in Iraq, investors might want to know the results of the coming elections.
For sure, political reasons played a role for changing the date of the bid round. Until a few months ago, the official schedule required that the final contract and tender protocol be issued by the end of May 2018 and that the submission of bids and the awards occur in June 2018 (see also BACCI, A., Iraq’s Fifth Licensing Round, in Iraq Business News, Dec. 20, 2017). Honestly, because Iraq has not been investing in the development of the border fields for the last 50 years, it’s is difficult to see what would have been the economic loss for Iraq’s government if Iraq had organized the auction two months later, i.e., in June, as it had previously planned. Two months would not have been a stark difference for the government, but it would have been a consistent difference for the I.O.C.s, which might have studied more completely the offered blocks and the new contract.
So, politics played a role. In Iraq, 320 members out of the 329 members of the Parliament are elected through the open list form of party-list proportional representation—the remaining 9 seats are reserved for the minorities. Iraq’s 18 governorates act as the constituencies. The ten onshore offered blocks are in the following Iraqi governorates: Basra, Diyala, Wasit, and Missan. In total, in May, these four governorates will be responsible for the election of 60 seats, or more than 18% of the seats (Basra, 25; Diyala, 14; Missan, 10; and Wasit, 11). However, at the same time, these governorates are home to the majority of Iraq’s most important oil fields (in particular Basra Governorate). And, because in Iraq the economy is dominated by the petroleum sector, which provides about 90% of government revenues and 80% of foreign exchange earnings, it’s easy to understand the pivotal economic role played by these governorates.
Moving forward the development of the additional blocks located in the above-mentioned governorates to before the elections may indeed provide a political support to Oil Minister Jabar Ali al-Luaibi who is a member of the Victory Alliance, which is led by Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi. In practice, holding the fifth licensing round would be a sort of additional tool to increase the chances of victory for a specific political group in the affected areas, because this move shows that the present government is concerned with the economic development of the above-mentioned governorates. And considering Iraq’s present fragile political environment, this political move has a certain logic. Now, according to the schedule, the deals must be signed on May 10. If they are not approved by the present government, it will be the task of the new government to approve them.
Considering these political reasons, it’s difficult to say whether we can consider the fifth licensing round finished and not just a politically useful stopgap. In any case, what is surprising is that important amendments to the structure of the offered service contract have been carried out with limited input from the industry and the stakeholders. In fact, the basic truth of the petroleum industry is that if a contractor is able to generate a return exceeding its planned internal rate of return (I.R.R.) threshold, it will go ahead with its investment. If the planned return is less than the I.R.R. threshold, the contractor will not invest.
This problem stood out very clear in 2009 during Iraq’s first licensing round. The day of the auction the result was negative because the companies did not see any profitability in what was offered. In practice, only after a few months of additional negotiations, was the government able to transform a failed licensing round into a success. What happened at that time was that the average cash outlay was renegotiated so that the I.O.C.s could have an improved profitability. And in just a few months, Iraq could sign contracts for the Rumaila field, the Zubair field, the West Qurna 1 field, and the Maysan field.
Moreover, after the end of the fifth licensing round, the Ministry of Oil correctly affirmed that the lack of bids for five exploration blocks— Zurbatiya and Shihabi on the border with Iran, Jebal Sanam and Fao on the border with Kuwait, and the offshore block—was also linked to additional difficulties, which could have increased the costs for the contractors. In fact, some blocks cover former battlefields (Zurbatiya and Shihabi), some have an infrastructural gap, and the offshore block lacks complete data.
Crescent Petroleum, a subsidiary of the multinational conglomerate Crescent Enterprises, is the first and the largest private upstream oil and gas company in the Middle East. It has operations in the U.A.E. and in the Kurdistan Regional Government (K.R.G., a.k.a. Iraqi Kurdistan). In the U.A.E., the company operates the Sharjah onshore concession and the Sir Abu Nu’ayr concession, while in the K.R.G. it operates the Khor Mor and the Chemchemal gas fields. In addition, Crescent Petroleum is the founder and the largest shareholder in Dana Gas, which is the first and largest publicly listed private-sector natural gas company in the Middle East.
Geo-Jade Petroleum is an oil exploration and production company with operations in Kazakhstan and Russia. This company started its oil and gas investments only in 2010—before the company was involved exclusively in real estate. Today, it is independently operating six exploration blocks and three development blocks. United Energy Group (U.E.G.) is an oil and gas exploration company having projects in Pakistan and Indonesia. In 2017, U.E.G. had an annual production of more than 4 million tons. After the acquisition of BP Pakistan in 2011, the company has expanded its operations in the country, and, today, U.E.G. and United Energy Pakistan Limited (U.E.P., U.E.G.’s Pakistani subsidiary) are the largest foreign E&P company and investor in Pakistan.
With reference to the contracts, the Ministry of Oil has introduced some amendments that have changed the structure of Iraq’s service contracts. During the previous four licensing rounds, Iraq had used service contracts in which there was a per-barrel fee remuneration linked to an R-Factor. The amended contract is different in that it sets a link between oil prices and the remuneration given to the I.O.C.s. At the same time, it introduces a 25% royalty on gross production.
In practice, out of the overall revenue, first, the contractors will pay a 25% royalty on gross production, second, they will recover the incurred costs according to a specific formula, third, they will split the remaining part, i.e., the net revenue share, with the government according to the percentage established at the time of the bid round, and fourth, they will pay the 35% corporate income tax (C.I.T.) on their percentage of net revenue share. Moreover, the amended contract does not consider any longer oil byproducts (for instance liquified petroleum gas) as companies’ revenue.
The key to understanding the new contractual framework is Article 19 of both the exploration, development, and production contract (E.D.P.C.) and of the development and production contract (D.P.C.). Art. 19 explains that in any quarter, Iraq’s involved regional oil company (R.O.C.) shall be entitled to a royalty of twenty-five percent (25%) of the deemed revenue, which is the value of net production in barrels of oil equivalent. With reference to the petroleum costs, Art. 19.5 explains that
[i]n respect of Petroleum Costs, in any Lifting Quarter due and payable Petroleum Costs shall be paid to Contractor to the extent of the Percentage of Net Deemed Revenue. The Percentage of Net Deemed Revenue shall be determined by reference to SOMO’s [the contract here means the State Oil Marketing Organization or its successors] average OSP [official selling price] during the Spending Quarter and in accordance with the following formula:
Percentage of Net Deemed Revenue= (Average OSP / 50) * (70%) * Net Deemed Revenue
The said formula shall be applied throughout the Term, provided that where the average OSP is equal to or less than twenty-one point five US Dollars (US$ 21.50) per Barrel, the Percentage of Net Deemed Revenue shall be thirty percent (30%) of Net Deemed Revenue and where the average OSP is equal to or greater than fifty US Dollars (US$ 50.0) per Barrel, the Percentage of Net Deemed Revenue shall be seventy percent (70%) of Net Deemed Revenue.
The percentage of net deemed revenue means the available portion of net deemed revenue allocated for the payment of the petroleum costs. The net deemed revenue means deemed revenue less royalty.
Then, the contractor shall be entitled to a remuneration equal to the product of the remuneration percentage bid and the remaining net deemed revenue. The remuneration percentage bid means the percentage of the remaining net deemed revenue bid by the contractor. And the remaining net deemed revenue means the net deemed revenue that remains after the payment of the petroleum costs to the extent of the percentage of net deemed revenue.
And then, the contractor shall pay the corporate income tax at a percentage of thirty-five percent (35%) on the actually received remuneration generated from the implementation of the contract to the General Taxation Commission in accordance with the Law No.19 for year 2010.
These are the remuneration percentage bids according to the six awarded blocks:
- Khashim Ahmer-Injana (gas, Diyala Governorate): 19.99%, Crescent Petroleum
- Naft Khana (oil and gas, Diyala Governorate): 14.67%, Geo-Jade
- Khider al-Mai (oil, Basra Governorate): 13.75%, Crescent Petroleum
- Gilabat-Qumar (gas, Diyala Governorate): 9.21%, Crescent Petroleum
- Huwaiza (oil, Missan Governorate): 7.15%, Geo-Jade
- Sindabad (oil, Basra Governorate): 4.55%, United Energy Group
A first consideration is that the percentage of the remuneration varies consistently according to the considered block. However, this should not be surprising because these blocks might well, for instance, have different geological characteristics. In fact, already with the technical service contracts used in the first four licensing rounds, the per-barrel fee was different according to each auctioned field. Now, with the new contract model, the Oil Ministry is trying to provide a fee that is based on commodity prices and costs.
At least on paper, the Oil Ministry should be able to give in this way more flexibility to its contracts. In fact, the three main factors that determine the amount of resource wealth linked to a petroleum field (oil and gas) are the produced volume; the price of the petroleum; and the involved exploration, development, and production costs. From an economic point of view, the best option for both the contractor and the government would be when the following three factors coexist: a high production level; low exploration, development, and production costs; and high oil prices in the international markets.
Thanks to the new contractual structure, the government would like to force the contractors to act in a more efficient manner, while at the same time, because the remuneration fee is based on the remuneration percentage bid, the contractor would now be affected positively by the increase and negatively by the decrease in oil prices. At the same time, the new contracts have a time limit concerning the requirement for the contractors to stop flaring. Iraq would like to stop completely flaring by 2021.
Iraq has currently a daily oil production of about 4.43 million barrels from Baghdad-controlled oil fields (March 2018). The country’s exports averaged 3.45 million barrels a day last month from the southern ports. According to a 5-year development plan, the government wants to reach a production of 6.5 million barrels per day by 2022.
Alessandro Bacci is an independent energy consultant in relation to business strategy and corporate diplomacy (policy, government, and public affairs). Much of his activity is linked to the MENA region, an area where he lived for four years. Alessandro is now based in London, United Kingdom (www.alessandrobacci.com), and he is a member of the Association of International Petroleum Negotiators (A.I.P.N.). A multilingual professional, Alessandro holds a Bachelor of Laws and Master of Laws from the University of Florence (Italy), a Master of Public Affairs from Sciences Po (France), and a Master in Public Policy from the Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy (Singapore).