By Ahmed Mousa Jiyad.
Any opinions expressed are those of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect the views of Iraq Business News.
Introduction
KRG’ gross oil export revenues, for 2017, stood at $7.9billion but it was left with only $3.9billion as net earnings.
When the Region receives less than half of its gross oil exports revenues, this is alarming situation indicating something has been seriously wrong and, thus, should be meticulously addressed in most transparent, truthful and evidenced-based manner. Otherwise, Kurdistan Region’s economy remains stranded in debt-trap through mortgaging future oil sales arrangements.
That is one of my conclusions after analyzing two half-yearly reports.
Deloitte, a known international firm, was appointed by the Regional Council for Oil and Gas Affairs (RCOGA) of the Kurdistan Regional Government in Iraq (KRG) to review oil production, export, consumption and revenue for 2014 through 2017.
The company, i.e. Deloitte, produced so far two half-yearly reports for 2017 covering KRG, “Oil production, export, consumption and revenue”. The first report was dated 13 January 2018 and covers the period 1 January to 30 June 2017; hereinafter refer to by H1-2017. The second was dated 31 July 2018 covering the period 1 July to 31 December 2017; hereinafter refer to by H2-2017.
After thoroughly analyzing these two reports I conclude that:
- they add very little qualitative or substantive improvements on previously published reports, though it took the company 22 months to produce a report for only one year;
- what was produced by Deloitte was far below the requirements of known transparency thresholds, e.g. EITI Standard, since too many important data and vital information were missing and not addressed;
- the fact that Deloitte adopts KRG formal views and uses data held and provided by MNR to produce its only one table of data, this surely tarnish Deloitte independency of reporting; and finally,
- these reports offer absolutely no analyses of the provided data, particularly their fiscal impacts on the economy of the Region.
This study is composed of four parts: part one provides brief description of the structure and components of Deloitte reports; part two discusses the integrity, credibility, transparency of the process and compliance with EITI Standard; part three unifies and analysis all data of the two half-yearly reports and part four offers concluding remarks.*
I-Structure of the report and its parts
The half-yearly report comprises three different parts that are produced and disseminated separately.
The first part is entitled and contains “Questions and Answers- Kurdistan Region – Iraq Oil & Gas Sector”, hereinafter referred to in this assessment as “Q&A part”.
This part is the longest and provides narratives on 27 selected topics; they mostly represent the official views of KRG and it is therefore, the same text in both half-yearly reports.
The purpose of this Q&A part is “to help readers better understand different sections of the report.”
The second part provides data on “Oil production, export, consumption and revenue” for the related period. This 3 page part comprises introduction, one data schedule/table and explanatory notes on the schedule.
The third part is one page of infographic with a few illustrative charts of the data provided by the second part. However, this part has not yet produced for the second half-yearly report.
Each part was produced in English, Kurdish and Arabic.
This assessment focuses primarily on the data contents of part two (in both half-yearly reports), since such data constitutes the core of the entire purpose of the report, and to the clarification given in “Q&A part”.
Before going further, a few words are due.
The tri-lingual report produced concurrently contributes to disseminate information among wider readership, particularly among the local citizens (mostly Kurdish) and other Iraqis (mostly Arabs).
Also, producing the report after six months’ time-lag (for 2017) is, in comparative sense, by far better than the National Secretariat of Iraq EITI-IEITI, which its last annual report was related to 2015!
Moreover KRG’ RCOGA anticipates that data for 1 January 2018 to 31 March 2018 to be publically available in August 2018.
Timewise, all these reports are commendable achievements that deserve support and encouragement.
Having said that, on the downside there are two remarks.
First, the related contract with Deloitte was signed, in a closed ceremony, early October 2016; intended to cover years 2014 to 2017. Hence, taking 22 months to produce one year report is hardly a commendable performance. Moreover, it is not known when the reports for the remaining three years (2014:2016) would be ready.
Second and most important, a thorough reading of the data, the methodology and provided explanation generates many more serious remarks, concerns and identifies missing vital items; as discussed below.
II-The Integrity, Credibility, Transparency of the Process and Compliance with EITI Standard
The World Bank proposed and sponsored Deloitte contract in 2016 and the Bank is partially financing Iraqi EITI (Extractive Industry Transparency Initiative) activities; in 2016, Iraq was an EITI compliant country.
Yet, Deloitte’ two half-yearly reports make no reference at all to EITI and they, in my humble views, are not in compliance with or adhere to the requirements, process and procedures outlined by EITI Standard. Needless to say, this Standard provides the most practical, comprehensive and widely adopted guide on transparency in the extractive industry. Moreover, transparency thematic issues and modalities of the Standard are much more than just data review as covered by the two reports under discussion.
In other words, absence of such compliance to EITI Standard would seriously undermine the credibility or claim of transparency of any report.
Therefore, it is legitimate to ask why the World Bank did not compel KRG and Deloitte to fully comply with EITI Standard in preparing the reports.
The above concern was premised on the observed immature claim of transparency and biased interpretation of these half-yearly reports. For example, KRG’MNR asserts Deloitte reports, demonstrate KRGs commitment to transparency and they set a precedent to further increase transparency. And by the way this intentional flawed interpretation of such reporting is not peculiar to KRG; Iraqi authorities expressed similar position when IEITI issued its first annual report and such wrong understanding generates a sense of self-satisfaction, mission accomplished and complacency that eventually led to suspending Iraq status with EITI.
When the funding for the contract was approved , “the “big four” international audit firms (Deloitte; PwC; EY; KPMG) were called upon to submit their technical and financial proposals, and which were consequently carefully reviewed and assessed, according to the international standards of the World Bank, in order to shortlist the chosen firm based on clear criteria and key performance indicators.”
Excellent! However, no information was provided on any of these “clear criteria and key performance indicators”, what are they, how the “big four” were assessed and ranked accordingly and timelines for bidding, selection and contracting activities among others. No answers!!
Obviously, that indicates an impacting lack of process transparency prior, during and after the selection. Strangely enough, the report claims, “The selection of Deloitte to carry out the review, meanwhile, was also made based on a diligent procurement and tendering process”
Without providing supporting evidence-based information on how the entire process was conducted, its diligence and transparency becomes questionable.
Each contract for such mission usually and preferably has, or should have, a detailed Terms of Reference-ToRs; this contract does not have any since no mention was ever made to the ToRs in any part of the reports. Why?
Absence of the ToRs for the mission probably explains the apparent confusion in the interchangeable use of different terms or concepts e.g. “review” “audit” “validation” as if they are the same. They are not!!
The following example exemplifies the confusion. In its welcoming statement on the first Deloitte report MNR says, “KRG can demonstrate its commitment to transparency in the reporting of oil production and revenue, and the reviews by Deloitte and EY will help to set a precedent to further increase transparency and strengthen independent auditing and verification in the Kurdistan Region.” (Bold added)
From technical, legal and operational perspectives these particular three terms or concepts are very different in their requirement and also implications. No doubt the “big four”, as reputable known international specialized entities, aware of the fundamental differences of the above three concepts; but the current two report do not demonstrate so!
The report asserts, “Our review was dependent on documentation provided by all stakeholders (oil producers, refineries, oil traders, the pipeline operator, and the KRG’s Ministry of Natural Resources), and the accuracy and completeness thereof.” (Bold added)
Fine! But again, the report did not produce any data or basic information that was provided by any of the above mentioned stakeholders. Refers to “stakeholders” without identifying them, except MNR, and without providing specific data pertaining to each of them shed big cloud of doubt on the accuracy and credibility of the “aggregated” data!!!
Colleting, verifying and validating process requires producing all data submitted, independently, by all involved stakeholders using specified templates, among other means. For example, all IEITI annual reports used such methodology though the number of involved stakeholders is much more than those in KRG and the magnitudes of production, export, domestic consumption and revenues are many folds that of KRG.
Moreover, the report assumed and relied on “the accuracy and completeness” of the provided documentation! But the report did not mention whether there was any test for such “accuracy and completeness”! Obviously, this “trust me/us” orientation and approach does not serve transparency very well, if at all!
The “trust me/us” approach was further evidenced by using another term, i.e. “misstatement”. By intention or omission, the two half-yearly reports affirm repeatedly and emphatically, “We did not identify any misstatements” regarding Oil export and consumption and oil sales during the covered year, 2017.
Such assertion and use of “misstatement” is surprising and causes suspicion. The reports deal with different stakeholders operating at various chains in the petroleum sector in the region; some operating internally while others externally; some are locals while others international etc., and surely each stakeholder has its own accounting, invoicing, contracting, reporting, auditing procedures. Experience, from IEITI (and also other EITI documents and reports) annual reports, tells that reconciliation of data provided by the stakeholders comprises many, significant and otherwise, “discrepancies”; the ToRs for such reports decide the “materiality threshold” for and the obligation to explain, by evidence-based, such “discrepancies”.
The point here, there are many reasons for “discrepancies” to occurs and that is usual and expected, but they have to be identified, quantified and explained. “Discrepancies” are not necessarily “misstatements”; thus using the later term by Deloitte is ratter unfortunate since it is conceptually and methodologically inaccurate, operationally misleading and politically comforting.
Currency issue is not addressed by the report, which says, “Apart from export sales and IOC bonuses, oil revenues are derived from local sales and from the sale of refined products.”
The report presents the values of these oil revenues that are derived from local sales (and the valuation of swap operations ) and from the sale of refined products in USD; but it did not mention anything regarding the used exchange rates between Iraqi Dinars-ID and USD. When locally generated revenues have significance in total revenues, then the issue of exchange rate becomes important variable that needs attention and recognition. Moreover, exchange rate could be a source of “discrepancies”. Deloitte should cover this issue in its forthcoming, or when revising, reports.
Oil production is the core of any report, particularly when it comes to transparency in the extractive industry. Though the title of the second part of the report starts with “oil production”, the report does not cover oil production at all!
Moreover, the Regional Council for Oil and Gas Affairs-RCOGA, in its statement on the second Deloitte report, “reiterates its commitment to the people of Kurdistan and stakeholders in the sector that the two international audit firms, Deloitte and Ernst & Young, will continue to independently review the oil and gas sector, inclusive of all the streams.” (Bold added). Clearly enough “all the streams” covers production and the expression “will continue” implies ongoing covering of oil production streams; Deloitte reports did not provide such cover.
But Deloitte report says, “production contributions for the individual fields is subject to additional reconciliation and verification procedures and this exercise is currently in progress”. Production from the fields is the main pillar for the entire data, so how reliable and trustworthy are such provided data when reconciliation and verification of production data are not done?
Strangely enough and despite the above remarks, the report asserts, as discussed above, “We did not identify any misstatements” in “oil export and consumption” and “oil sales”; oil production was not covered!
On this issue the report says, “It should be noted that currently Deloitte did not report on the KRG’s oil production data, pending the completion of a historical oil production reconciliation for 2014, 2015 and 2016.”
The above statement could be interpreted that oil production reconciliation for 2017 has been done and ready. If so, what are the compelling justifications for not disclosing them in the released two reports?
In addition to the above rather substantive remarks, there are others that tarnished the quality of Deloitte reports.
A matter that worth mentioning is related to “oil sales” item. In the report for the first half of 2017 it is mentioned “oil sales data and the net amount received in the month by the KRG”, while the corresponding item in the report for the second half refers to “oil sales data and the net amount received in the period by the KRG.” (Bold added). If that is an error, it must be corrected, but if it is not then it should be explained.
The reports that took 22 months to cover, partially, 2017, provides no clear work plan, its phases, timeliness, consultation process (with whom, when, about what etc) and whether the final text of either of the two half yearly reports were subjected to any sort of consultation process with or discussing the findings; or they were presented on the base of “trust me/us”.
The reports refer to the Regional Council for the Oil & Gas Affairs by two acronyms: (RCOGA) and (RCOG); A possible sign of inconsistency or carelessness.
Apart from the fact that most contents of “Q&A part” represent KRG official views, except a few relating to Deloitte, this part of the report contains a couple of referencing inaccuracies e.g. in items 11 and 13.
Finally, the report warns, “No party, other than the RCOG, is entitled to rely on this report for any purpose whatsoever”. In addition to such statement is clearly anti-transparency, it emphatically contravenes items 18 and 19 in the “Questions and Answers- Kurdistan Region – Iraq Oil & Gas Sector” part of the reports.
In conclusion and based on the above remarks I am of the opinion that KRG, RCOGA and Deloitte should consider seriously these remarks and make the necessary modification, correction, explanation, clarification and addition, among others to improve the quality, credibility, integrity and usefulness of the reports.
Based on the above remarks there is apparent doubts on the integrity and credibility of the process that need addressing by Deloitte, KRG and RCOG/A.
I will turn now to data analysis of the two reports.
III-Data Analysis and Assessment
As mentioned earlier the second part in both half-yearly reports provides data on “Oil production, export, consumption and revenue” for the related period. This three page part comprises introduction (one page of almost the same text in both reports, except the dates of the covered period), one schedule/table comprising data (one page) and explanatory notes on the schedule (one page).
The one and only schedule covers data relating to four main items, each has many sub-items. The main items are: Oil Exports and Consumption; Pipeline Export Sales Analysis; Trucking Export Sales Analysis and Financial Flows. The following offers analyses for these four main items.
Before proceeding further, it is useful highlighting the following:
First, H1-2017 report says, “All figures in Schedule 1, … , are based on the records held by the KRG”, while H2-2017 report says, “All figures in Schedule 1, … , are based on the records provided by stakeholders to the KRG.”
This is clearly a contradiction to what Deloitte asserts, “Deloitte corresponded directly with the various stakeholders to obtain and verify the information contained in Schedule 1”
Second and as mentioned earlier, the reports do not provide data on production though the title of the part of the report mentions “oil production”; this constitutes a major flaw;
Third, the reports do not contain analytical assessment of the covered data, I have done that hereunder;
Fourth, the two parts were not combined in a yearly 2017 report or provide the annual data in one table, so I have to do that;
Fifth, the Q&A part provides no explanation or clarification of the items covered by this part; it only lists them.
First: Oil Exports and Consumption
This item covers eight sub-items and a total with half yearly aggregated data; all data are expressed in number of barrels (bbls)
To begin with there is a methodological and coverage problem relating to item “crud allocated to oil producers”;
First, it is neither included in the export data nor in the consumption data. So where had these volumes gone?
Second, why this item was not mentioned in the second half-yearly report? Where there no crude allocated to the oil producers or it was reporting error? The report for the second half clarifies this, “Total exports and consumption does not include: (1) crude oil and condensate allocated as compensation to producers; and (2) condensate sales by Dana Gas. These amounts have not been included in total exports and consumption on Schedule 1 as the MNR is not entitled to any of the proceeds from the sale or consumption of this crude oil / condensate.” But again, that report gives no data on these two types of excluded volumes!! Also, Deloitte did not explain why it includes and quantifies this item i.e. “crud allocated to oil producers” in H1-2017 report and avoids that in H2-2017; is there any politics here?
Also different categorization, regarding “Local sales, Sales to refineries and swap” was applied in the H2-2017 report making it difficult, or meaningless, to make sub-item comparison.
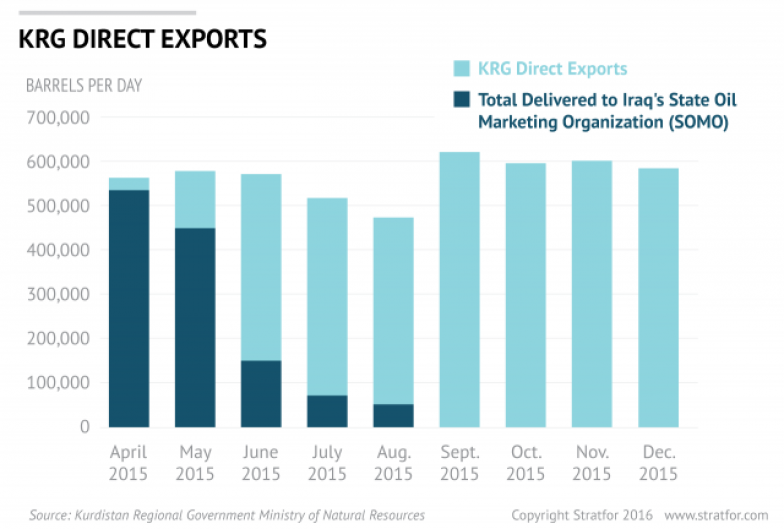
On the aggregate, KRG total oil “exported & consumed” in 2017 was 201.85 million barrels (bbls), 55% of which was in the first half of the year while the rest in the second half. This 10 percentage points could be attributed to post-referendum in the Region of September that year and retaking of Kirkuk by federal authority.
2017 oil export occurred through pipelines and trucks totaled over 187 million bbls (94.8% of which was through pipelines). It is worth mentioning that piped export includes “KRG and NOC contribution”, as the reports mention, but they do not quantify both contributions. On a periodic comparison, piped oil export declined from 95.8 million bbls in first half of 2017 to 81.5 million bbls in the second half.
Second; Pipeline Export Sales Analysis
This part of the report provides data on net oil lifted by the buyers through pipeline, gross value of crude oil sold and average barrel price.
Comparing the data in this section with the corresponding data in the first section indicates discrepancies, which the report attributes to “Increase (decrease) in storage at oil terminal”
Volume of net oil lifted by the buyers through pipelines totaled 177.773 million bbls for the entire year. However, it declined from 95.937 million bbls in the first half to 81.836 million in the second half; a decline by 14.7%.
These volumes had “gross value” of $7.61 billion, with only 7.1% decline in second half of the year compared with first half; that is obviously explained by oi price improvement, as discussed next.
Average oil price increased from $41.297/b to $44.584/b in the two parts of the year respectively.
Third, Trucking Export Sales Analysis
Unlike piped oil export, trucking exports registered significant improvements for all three sub-items in second half of 2017 comparing with the first half. Volume-wise, trucked exports increased from 4.231million bbls to 5.147 million bbls in the two halves of the year. Gross value of these volumes almost doubled: increased from $108million to $205million. Similarly, average price a barrel increased from $25.452 to $39.883 in the same period.
What should be highlighted is that pipeline-truck oil price differentials for the two halves of the year declined, in favor of pipeline exports, from $15.845/b to $4.701/b. In the meantime trucking transportation costs per barrel was $10 during H2-2017.
This calls for specific research to better understanding trucking export economics; why there was such a significant price differentials, what are the main causes, who are the trucking stakeholders and was there influential political connection with or interests for individuals, groups or parties in KRG and or Turkey.
Fourth, Financial Flows
Data provided in this section is probably the most vital for understanding fiscal conditions and performance of the petroleum sector in Kurdistan Iraq.
This section contains 11 items without, as mentioned earlier, comparison, analyses and explanation, except 3 notes on data relating to H2-2017 report. However, notes provided on the other three sections of this report should be kept in mind.
To avoid possible confusion or mixing-up, I will use the same terminology used by the report as titles for the sub-items of the financial flows, but give and use in the analyses what each term could mean. But I must mention, at the outset, the number of items under this section in Schedule 1 are more, by two items, than those listed in the Q&A part; and again, no explanation was provide. Thus, this is added flaw of the report let be inconsistency or inaccuracy.
Gross value of crude oil sold (Piped and Trucked exports) USD
The report uses the above term, which implies valuation, but I will take this as gross revenues; the rationale is premised on the fact that what matters is the stream of revenues (gross and net) from exported (or sold) oil. Evidence is provided by item 10 in this section, which asserts “Net cash balance received..”. So, why Deloitte uses such ambiguous terminology??
Also this item deals with “exports”, but what about revenues from oil and refined product sold and swapped locally (as mentioned in “Oil Exports and Consumption” addressed above)!
Gross oil export revenues for 2017 totaled little more than $7.9billion. This would give an average price of $42.338/b.
Comparing these to the corresponding average oil prices realized by SOMO of $49.185/b respectively would give significant price-differentials in favor of federally marketed oil of $6.245/b; a 14.8% price differentials represent voluminous financial losses for KRG economy, which suffers from deep fiscal crisis. Why and what for!?
Deloitte justifies these price differentials this way, “In the case of KRG, a considerable portion of its oil is heavy and sour, which partly explains why it is sold at a discounted price. Competitiveness is another reason, whereby the disagreement with Baghdad and the limited exporting routes has meant that KRG had to render its oil exports more competitive in order to sell its output and generate critical funds for the Region.”
Again, Deloitte conceded to KRG /MNR views without discussing the economic and financial implications of such price differentials on the local economy of the region.
Net movement in buyer account balances (excluding advance payments) USD
Probably this item deals with payment made by KRG to what it borrowed from the oil buyers outside the advanced payment arrangements. But how, what deals and which oil buyer? No answer was provided!
This payment was mounted to $634 million and cuts 8% of gross revenues; too much for debt repayment!
Moreover, Deloitte says nothing regarding the remaining balance of these debts (or estimate the balance of buyer account)!!
Interest and other charges from the buyers (USD)
This also represents payment by KRG to oil buyers in interest on debt from these buyers and “other charges”! These “other charges” were explained for the second part of the year only.
KRG paid more than $108million (almost 1.4% of its gross revenues) to oil buyers for “interest and other charges”.
The report mentions $13.2million in H2 2017 as interest charges and fees, but says nothing regarding such payment for the first half of the year; or the rate of interests and the balance of debt.
Payments made to oil producers by, or on behalf of the KRG (USD)
This is major item that cuts close to $1.2 billion (or 15.1%) of gross oil export revenues of the Region.
However, the report does not specify why and for what these payment were made: for cost oil, for profit oil, for previous entitlements etc. Also, which producers were paid and how much for each were not mentioned.
Payments made to third parties by, or on behalf of the KRG (USD)
Another major cut of $1.3billion (16.8% from KRG gross revenues) was paid to undisclosed “Third parties”; who are they? How many of them? Where are they? Why did they take such a significant chunk from region revenues?
This is no simple matter; it symbolizes utter secrecy and trivializes and makes mockery of transparency claims that are repeated throughout these reports.
Payments made against arbitration settlement (USD)
KRG paid, from its export revenues of the second half of the year, more than $518 million in connection with an arbitration settlement agreement. The report did not disclose the name of the parties to that agreement or total payable settlement; it only says “The total settlement was higher than this amount and the balance was provided from other KRG revenue sources.” Another evidence for lacking transparency!
Net cash balance received by the KRG for the period sales USD
In addition to the above, other amounts of $247million were deducted from this year gross revenues, leaving only $3.892billion as net cash balance received by KRG; meaning KRG received only 49.1% of gross revenues.
But KRG received $1.436billion in “Additional advance payments made by buyers against future sales”; thus, the Region’s economy remains stranded in debt-trap by mortgaging future oil sales! Ironically, Deloitte reports and the Q & A part say nothing on these “advanced payments” and their specifics!
Concluding Remarks
KRG/MNR used to issue monthly reports the last of which was for October 2016. That practice was ended, paving the way for Deloitte to do the job, presumably better!
After 22 months, Deloitte’s report for only one year adds, if any, very little qualitative or substantive improvements on MNR’ previous reports.
What was offered by Deloitte’s reports, like those of MNR, are far below the requirements of known transparency thresholds, e.g. EITI Standard. Hence, claims of transparency by these reports were absolutely not supported by the contents of these reports; too many important data and vital information were not addressed.
Deloitte adopts KRG/MNR views and uses data held and provide by KRG/MNR to produce its only one table of data; this surely tarnish Deloitte independency of reporting.
When the Region receives less than half of its gross oil exports revenues, this is alarming situation indicating something has been seriously wrong and, thus, should be meticulously addressed in most transparent, truthful and evidenced-based manner. Otherwise, Kurdistan Region’s economy remains stranded in debt-trap through mortgaging future oil sales arrangements.
* For work necessities, all references and footnotes were removed
Norway
7 August 2018
Please click here to download Ahmed Tabaqchali’s full report in pdf format.
Mr Jiyad is an independent development consultant, scholar and Associate with the former Centre for Global Energy Studies (CGES), London. He was formerly a senior economist with the Iraq National Oil Company and Iraq’s Ministry of Oil, Chief Expert for the Council of Ministers, Director at the Ministry of Trade, and International Specialist with UN organizations in Uganda, Sudan and Jordan. He is now based in Norway (Email: mou-jiya(at)online.no, Skype ID: Ahmed Mousa Jiyad). Read more of Mr Jiyad’s biography here.